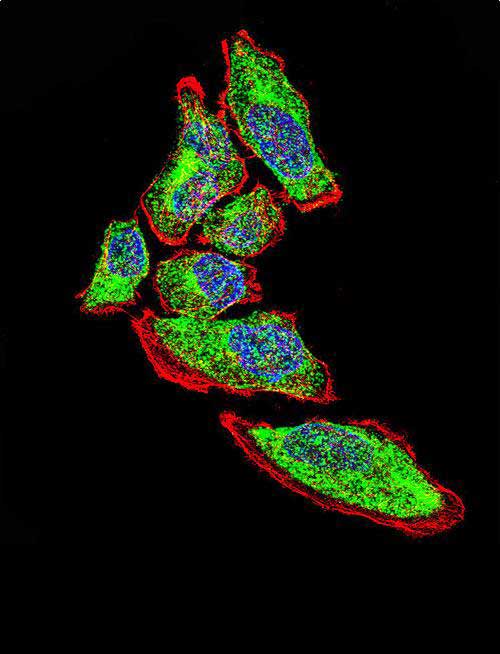
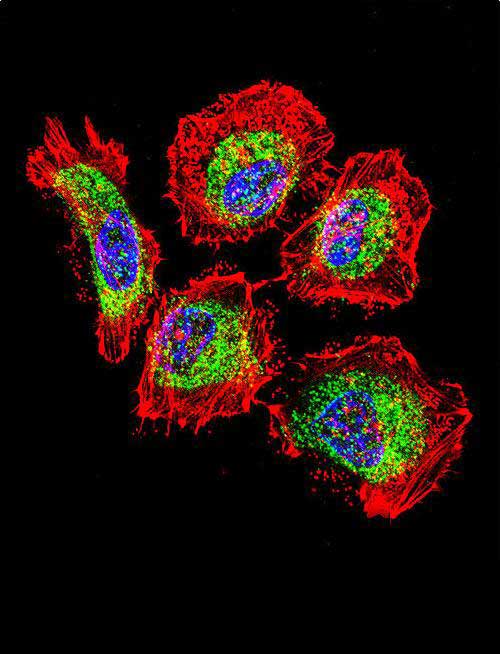
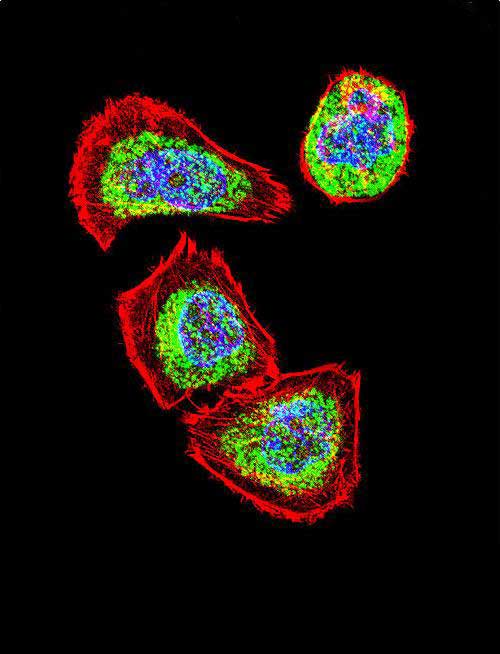
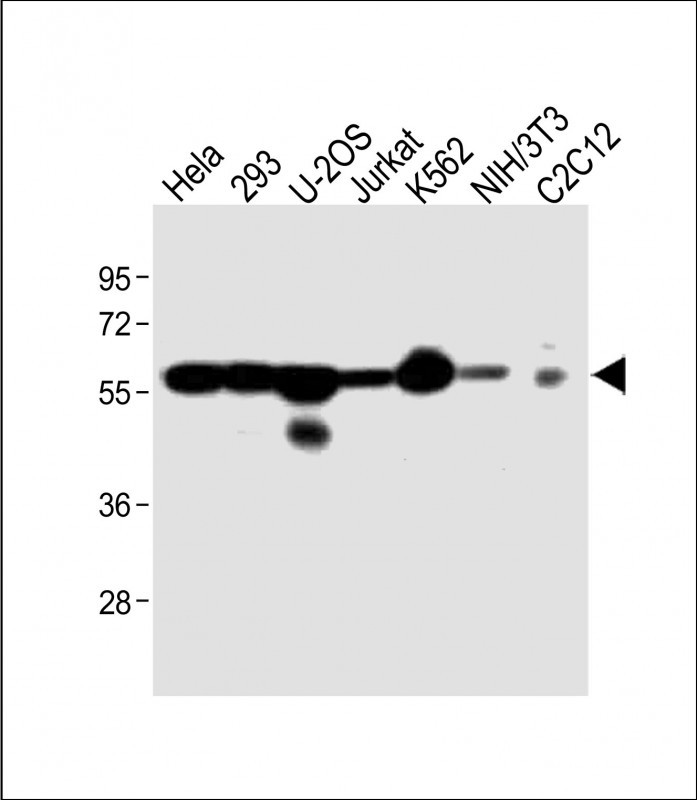
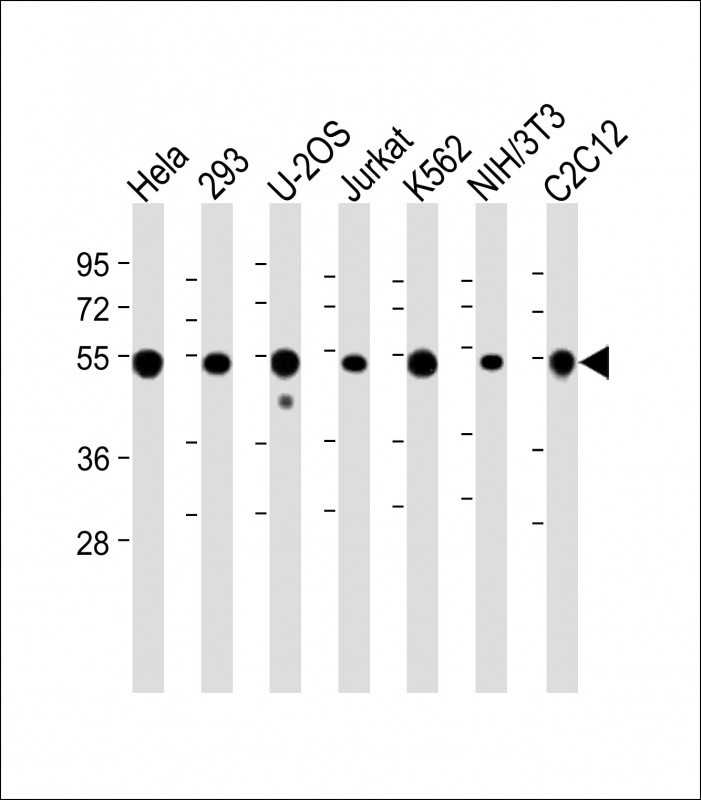
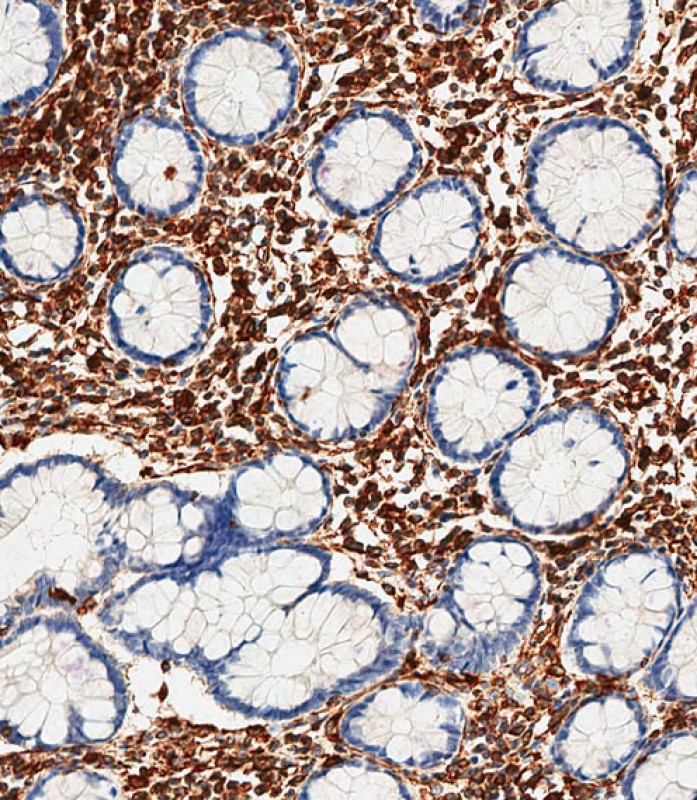
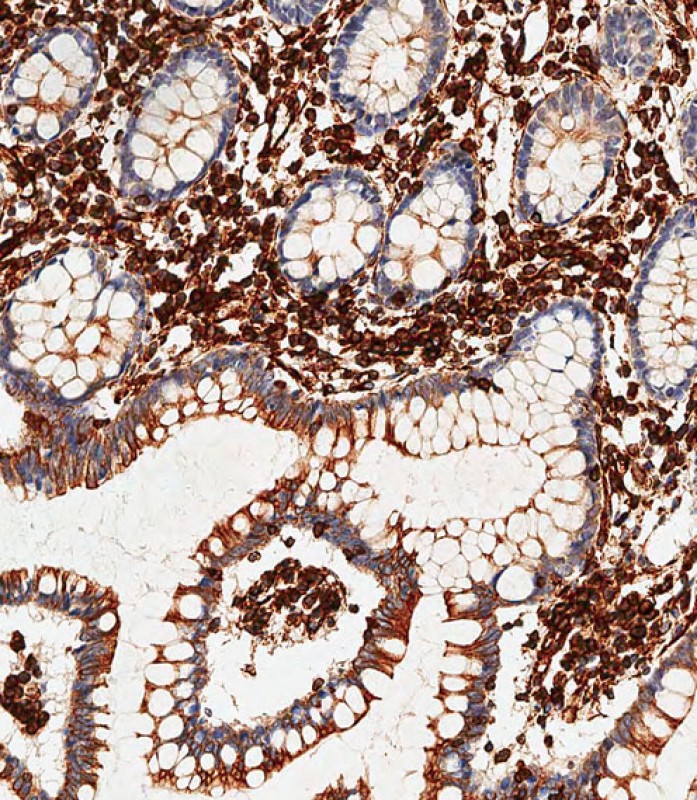
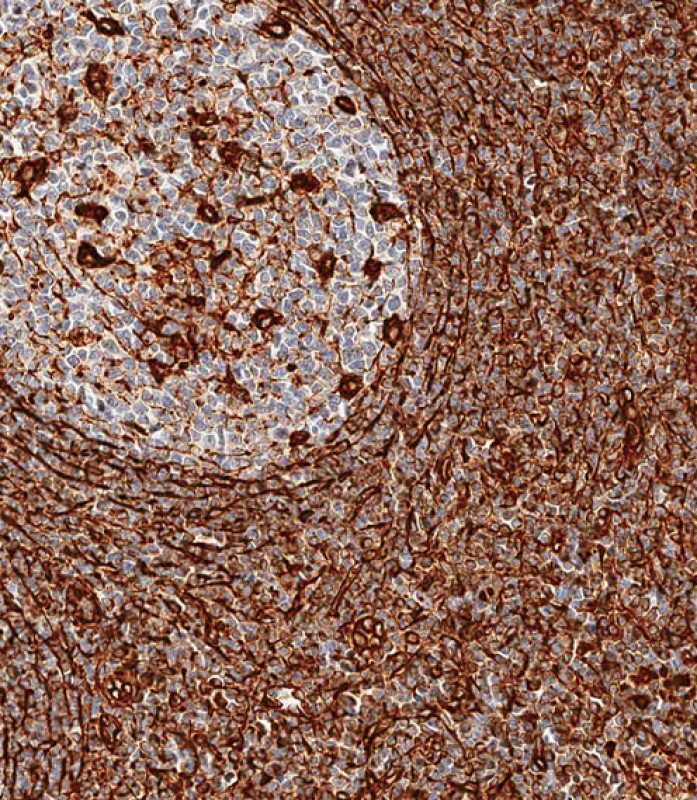
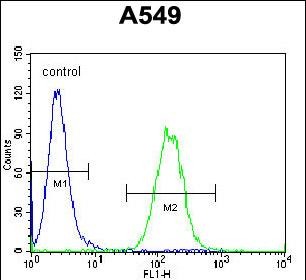
Application 
| WB, IF, FC, IHC-P-Leica, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P08670 |
| Other Accession | NP_003371.2 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Clone/Animal Names | RB41034 |
| Calculated MW | 53652 Da |
| Gene ID | 7431 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Vimentin, VIM |
| Target/Specificity | This Vimentin antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with human Vimentin recombinant protein. |
| Dilution | IF~~1:50 WB~~1:2000 IHC-P-Leica~~1:500 FC~~1:50 |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Vimentin Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | VIM (HGNC:12692) |
|---|---|
| Function | Vimentins are class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is attached to the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, either laterally or terminally. Plays a role in cell directional movement, orientation, cell sheet organization and Golgi complex polarization at the cell migration front (By similarity). Protects SCRIB from proteasomal degradation and facilitates its localization to intermediate filaments in a cell contact-mediated manner (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus matrix {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31000}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20152} |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in fibroblasts, some expression in T- and B-lymphocytes, and little or no expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Expressed in many hormone-independent mammary carcinoma cell lines. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes a member of the intermediate filament family. Intermediate filamentents, along with microtubules and actin microfilaments, make up the cytoskeleton. The protein encoded by this gene is responsible for maintaining cell shape, integrity of the cytoplasm, and stabilizing cytoskeletal interactions. It is also involved in the immune response, and controls the transport of low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-derived cholesterol from a lysosome to the site of esterification. It functions as an organizer of a number of critical proteins involved in attachment, migration, and cell signaling. Mutations in this gene causes a dominant, pulverulent cataract.
References
Kers, J., et al. Transplantation 90(5):502-509(2010)
Pinheiro, A.P., et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 153B (5), 1070-1080 (2010) :
Korita, P.V., et al. Anticancer Res. 30(6):2279-2285(2010)
Martins-de-Souza, D., et al. J Psychiatr Res (2010) In press :
Li, M., et al. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 29, 109 (2010) :