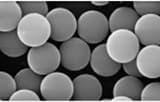
Microspheres, defined as spherical particles with diameters typically ranging from 1 to 1000 μm, represent a crucial class of materials in various scientific and technological fields. Microspheres have attracted considerable attention due to their unique properties, including high surface area, controllable size, and spherical morphology.
Properties of Microspheres
-
Surface Area and Porosity: Microspheres have a high surface area-to-volume ratio, enhancing their ability to interact with their surroundings. Porous microspheres further increase the surface area, facilitating the adsorption and encapsulation of molecules.
-
Controlled Size and Morphology: The size and shape of microspheres can be precisely controlled during synthesis, allowing for tailored applications. Uniform size distribution ensures consistent behavior in applications such as drug delivery and diagnostics.
-
Biodegradability and Biocompatibility: Microspheres made from biodegradable polymers are biocompatible, making them suitable for biomedical applications.
-
Mechanical Strength: The mechanical properties of microspheres, such as their stability under pressure and shear stress, are crucial in applications like drug delivery and tissue engineering.
-
Optical Properties: Microspheres can be designed to exhibit specific optical properties, such as fluorescence or light scattering, enabling their use in imaging and diagnostics.
Advanced Applications
Microspheres find applications across a wide range of fields.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Microspheres are widely used as drug carriers for controlled and targeted drug delivery. By encapsulating drugs within microspheres, sustained release and site-specific delivery can be achieved, improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Tissue Engineering: Microspheres serve as scaffolds for cell growth and tissue regeneration. They can be designed to mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) and provide structural support for cells to adhere, proliferate, and differentiate.
- Catalysis: Microspheres with high surface area and tailored surface chemistry are used as catalysts in various chemical reactions. They offer advantages such as enhanced reaction rates, selectivity, and catalyst recovery.
- Cosmetics: Used in sunscreens and anti-aging creams.